Georeferenciar una imagen / raster es el proceso de localizar espacialmente una imagen para que cada pixel este asociado a una posición. Este proceso es ampliamente conocido en QGIS con su complemento de Georeferenciación pero tambien puede ser realizado por Python y Rasterio.
El proceso de georeferenciar en Python tiene la ventaja que puede realizar el proceso repetidas veces sin necesidad de definir los puntos de control cada vez; también te permite añadir / quitar puntos de control y ver el impacto en el arreglo de transformación. Este tutorial muestra el proceso completo de georeferenciación de un mapa nacional sobre 3 puntos cuyas coordinadas de pixel han sido extraídas del utilitario Paint de Windows, el tutorial también exporta el raster asignando un sistema de referencia.
Tutorial
#import required libraries
import rasterio
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from rasterio.plot import show#open ungeoreferenced raster
unRefRaster = rasterio.open('data/Peligros_Geologicos.jpg')
unRefRasterC:\Users\saulm\anaconda3\Lib\site-packages\rasterio\__init__.py:317: NotGeoreferencedWarning: Dataset has no geotransform, gcps, or rpcs. The identity matrix will be returned.
dataset = DatasetReader(path, driver=driver, sharing=sharing, **kwargs)
<open DatasetReader name='data/Peligros_Geologicos.jpg' mode='r'>#show raster band values
unRefRaster.read(1)array([[255, 255, 255, ..., 255, 255, 255],
[255, 255, 255, ..., 255, 255, 255],
[255, 255, 255, ..., 255, 255, 255],
...,
[255, 255, 255, ..., 255, 255, 255],
[255, 255, 255, ..., 255, 255, 255],
[255, 255, 255, ..., 255, 255, 255]], dtype=uint8)#show raster
show(unRefRaster)#show raster shape
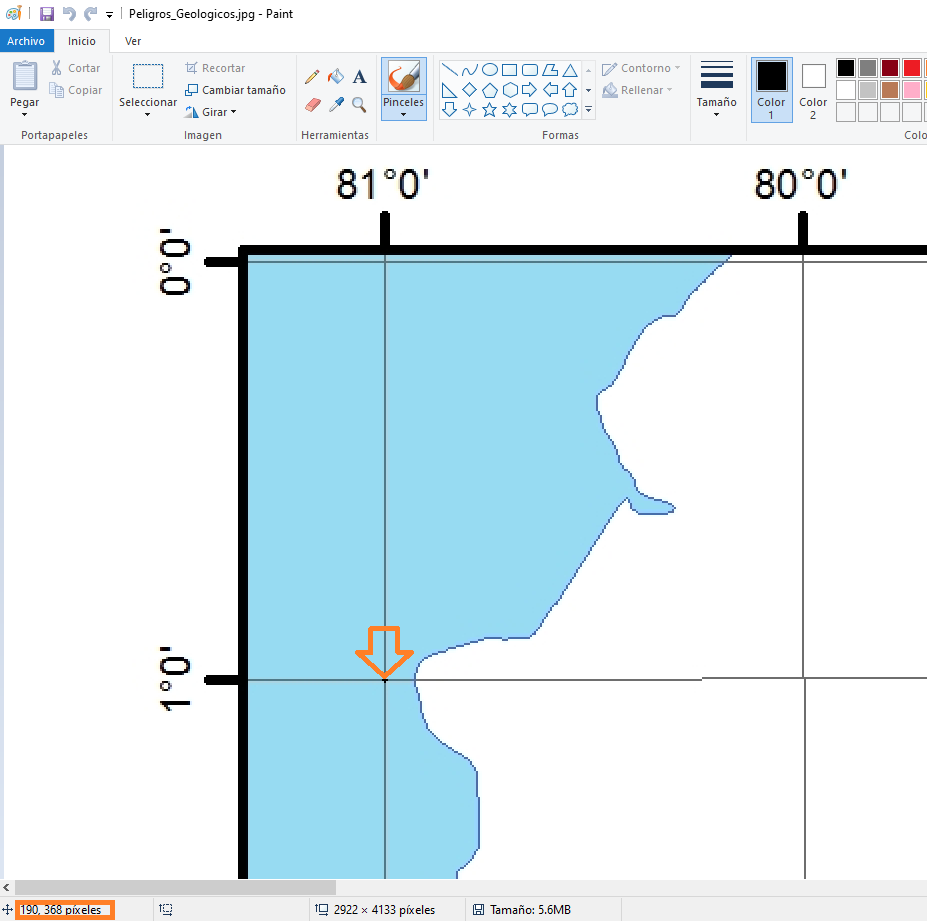
unRefRaster.read(1).shape(4133, 2922)Insert control points from coordinates captured in paint
Control point 1
point1 = rasterio.control.GroundControlPoint(row=368, col=190, x=-81, y=-1)
point1GroundControlPoint(row=368, col=190, x=-81, y=-1, id='5a920799-66fd-469b-b8f5-8ad0f50194dd')Control point 2
point2 = rasterio.control.GroundControlPoint(row=3497, col=239, x=-81, y=-16)
point2GroundControlPoint(row=3497, col=239, x=-81, y=-16, id='e74eee05-5a73-4632-a863-cf80dd0150b3')Control point 3
point3 = rasterio.control.GroundControlPoint(row=3706, col=2645, x=-69, y=-17)
point3GroundControlPoint(row=3706, col=2645, x=-69, y=-17, id='75f9378c-a918-4a45-a7f8-7f662578e132')#list of selected gcps
points = [point1, point2, point3]
points[GroundControlPoint(row=368, col=190, x=-81, y=-1, id='5a920799-66fd-469b-b8f5-8ad0f50194dd'),
GroundControlPoint(row=3497, col=239, x=-81, y=-16, id='e74eee05-5a73-4632-a863-cf80dd0150b3'),
GroundControlPoint(row=3706, col=2645, x=-69, y=-17, id='75f9378c-a918-4a45-a7f8-7f662578e132')]#get transformation array from points
transformation = rasterio.transform.from_gcps(points)
transformationAffine(0.004994325053839821, -7.821090688339848e-05, -81.92014014649648,
7.980704784024951e-07, -0.00479387635201452, 0.7639948641504404)#define output raster
outputPath = 'data/georefRaster.tif'#create raster and write bands
with rasterio.open(
outputPath,
'w',
driver='GTiff',
height=unRefRaster.read(1).shape[0],
width=unRefRaster.read(1).shape[1],
count=3,
dtype=unRefRaster.read(1).dtype,
crs=rasterio.crs.CRS.from_epsg(4326),
transform=transformation,
) as dst:
dst.write(unRefRaster.read(1), 1)
dst.write(unRefRaster.read(2), 2)
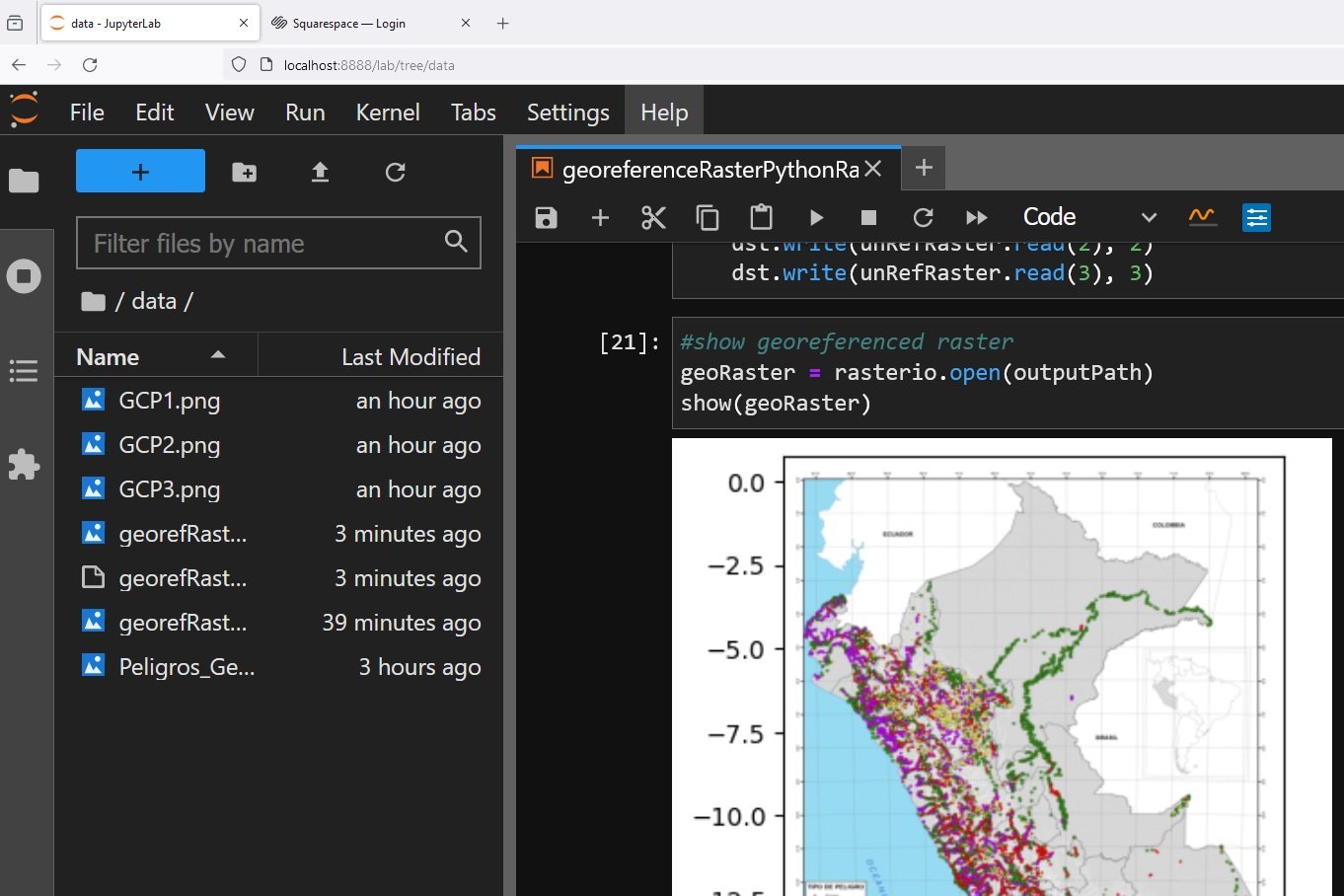
dst.write(unRefRaster.read(3), 3)#show georeferenced raster
geoRaster = rasterio.open(outputPath)
show(geoRaster)