Python es un lenguaje de programación capaz de realizar cálculos para estudios hidrológicos y evaluaciones de recursos hídricos. Hemos realizado un tutorial para la determinación de la curva volumen-elevación del lago Patillas en Puerto Rico con Python y bibliotecas numéricas / espaciales como Numpy y Rasterio. Finalmente, los resultados se compararon con la curva de volumen-elevación de una evaluación del USGS.
El procedimiento se realizó para un lago, pero se puede aplicar fácilmente a cualquier reservorio o cuerpo de agua cuando la elevación del fondo está disponible como un archivo ráster.
Tutorial
Código
Este es el código utilizado en el tutorial:
#Import required libraries
import rasterio
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.axes_grid1 import make_axes_locatableOpen raster file
lakeRst = rasterio.open('../Rst/lakeBottomElevation.tif')
lakeRst.count1#raster resolution
lakeRst.res(0.5, 0.5)#all raster crs info
lakeRst.crs.wkt'PROJCS["NAD83(2011) / Puerto Rico and Virgin Is.",GEOGCS["NAD83(2011)",DATUM["NAD83_National_Spatial_Reference_System_2011",SPHEROID["GRS 1980",6378137,298.257222101,AUTHORITY["EPSG","7019"]],AUTHORITY["EPSG","1116"]],PRIMEM["Greenwich",0,AUTHORITY["EPSG","8901"]],UNIT["degree",0.0174532925199433,AUTHORITY["EPSG","9122"]],AUTHORITY["EPSG","6318"]],PROJECTION["Lambert_Conformal_Conic_2SP"],PARAMETER["latitude_of_origin",17.8333333333333],PARAMETER["central_meridian",-66.4333333333333],PARAMETER["standard_parallel_1",18.4333333333333],PARAMETER["standard_parallel_2",18.0333333333333],PARAMETER["false_easting",200000],PARAMETER["false_northing",200000],UNIT["metre",1,AUTHORITY["EPSG","9001"]],AXIS["Easting",EAST],AXIS["Northing",NORTH],AUTHORITY["EPSG","6566"]]'Get raster values as Numpy array
lakeBottom = lakeRst.read(1)#raster sample
lakeBottom[:5,:5]array([[-3.4028235e+38, -3.4028235e+38, -3.4028235e+38, -3.4028235e+38,
-3.4028235e+38],
[-3.4028235e+38, -3.4028235e+38, -3.4028235e+38, -3.4028235e+38,
-3.4028235e+38],
[-3.4028235e+38, -3.4028235e+38, -3.4028235e+38, -3.4028235e+38,
-3.4028235e+38],
[-3.4028235e+38, -3.4028235e+38, -3.4028235e+38, -3.4028235e+38,
-3.4028235e+38],
[-3.4028235e+38, -3.4028235e+38, -3.4028235e+38, -3.4028235e+38,
-3.4028235e+38]], dtype=float32)#replace value for np.nan
noDataValue = np.copy(lakeBottom[0,0])
lakeBottom[lakeBottom==noDataValue]= np.nan
plt.figure(figsize=(12,12))
plt.imshow(lakeBottom)
plt.show()Lake volume calculation
# get raster minimum and maximum
minElev = np.nanmin(lakeBottom)
maxElev = np.nanmax(lakeBottom)
print('Min bottom elevation %.2f m., max bottom elevation %.2f m.'%(minElev,maxElev))
# steps for calculation
nSteps = 20
# lake bottom elevation intervals
elevSteps = np.round(np.linspace(minElev,maxElev,nSteps),2)
elevStepsMin bottom elevation 44.10 m., max bottom elevation 67.55 m.
array([44.1 , 45.33, 46.56, 47.8 , 49.03, 50.27, 51.5 , 52.74, 53.97,
55.21, 56.44, 57.67, 58.91, 60.14, 61.38, 62.61, 63.85, 65.08,
66.32, 67.55])# definition of volume function
def calculateVol(elevStep,elevDem,lakeRst):
tempDem = elevStep - elevDem[elevDem<elevStep]
tempVol = tempDem.sum()*lakeRst.res[0]*lakeRst.res[1]
return tempVol# calculate volumes for each elevation
volArray = []
for elev in elevSteps:
tempVol = calculateVol(elev,lakeBottom,lakeRst)
volArray.append(tempVol)
print("Lake bottom elevations %s"%elevSteps)
volArrayMCM = [round(i/1000000,2) for i in volArray]
print("Lake volume in million of cubic meters %s"%volArrayMCM)Lake bottom elevations [44.1 45.33 46.56 47.8 49.03 50.27 51.5 52.74 53.97 55.21 56.44 57.67
58.91 60.14 61.38 62.61 63.85 65.08 66.32 67.55]
Lake volume in million of cubic meters [0.0, 0.0, 0.13, 0.38, 0.68, 1.02, 1.4, 1.83, 2.31, 2.88, 3.56, 4.3, 5.1, 5.97, 6.91, 7.92, 8.99, 10.12, 11.3, 12.54]# plot values
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(12,5))
ax.plot(volArrayMCM,elevSteps,label='Patillas lake')
ax.grid()
ax.legend()
ax.set_xlabel('Volume MCM')
ax.set_ylabel('Elevation (masl)')
plt.show()# plot values
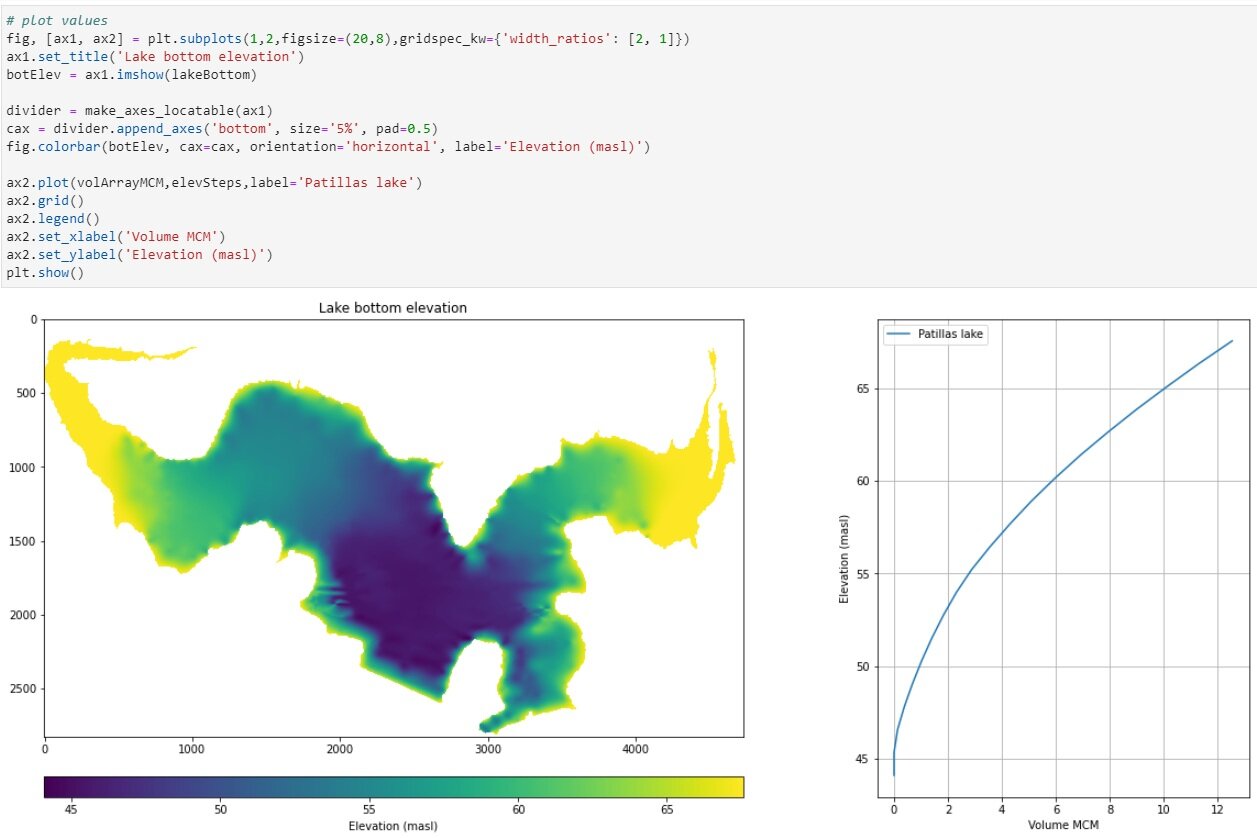
fig, [ax1, ax2] = plt.subplots(1,2,figsize=(20,8),gridspec_kw={'width_ratios': [2, 1]})
ax1.set_title('Lake bottom elevation')
botElev = ax1.imshow(lakeBottom)
divider = make_axes_locatable(ax1)
cax = divider.append_axes('bottom', size='5%', pad=0.5)
fig.colorbar(botElev, cax=cax, orientation='horizontal', label='Elevation (masl)')
ax2.plot(volArrayMCM,elevSteps,label='Patillas lake')
ax2.grid()
ax2.legend()
ax2.set_xlabel('Volume MCM')
ax2.set_ylabel('Elevation (masl)')
plt.show()Comparison with the USGS survey
From this pu
patVol = pd.read_csv('../Txt/patillasVolume.csv')
patVol.head()| OBJECTID | Pool_Elevation_m | Storage_capacity_mcm | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 67.55 | 12.96 |
| 1 | 2 | 66.55 | 11.79 |
| 2 | 3 | 65.55 | 10.68 |
| 3 | 4 | 64.55 | 9.64 |
| 4 | 5 | 63.55 | 8.70 |
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(12,5))
ax.plot(volArrayMCM,elevSteps,label='Patillas lake',ls= '-.')
ax.plot(patVol['Storage_capacity_mcm'],patVol['Pool_Elevation_m'],label='Patillas lake - USGS Survey')
ax.grid()
ax.legend()
ax.set_xlabel('Volume MCM')
ax.set_ylabel('Elevation (masl)')Text(0, 0.5, 'Elevation (masl)')Datos de entrada
Puede descargar los datos de entrada desde este enlace.